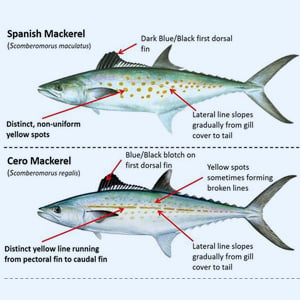
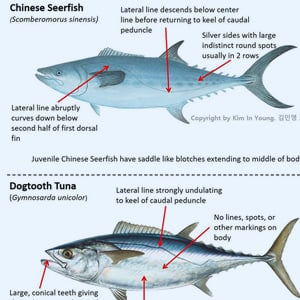
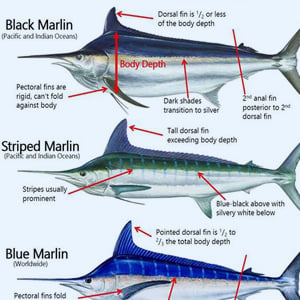
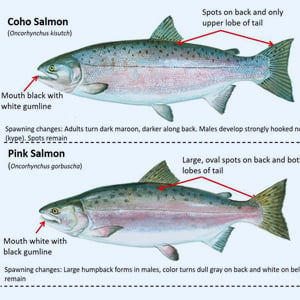
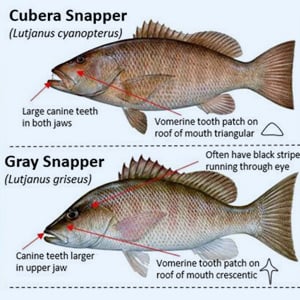
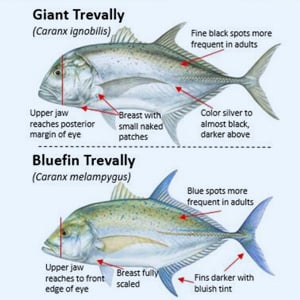
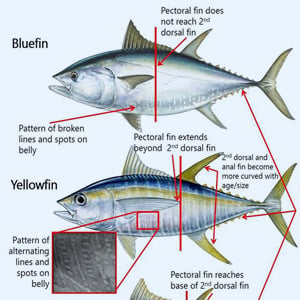
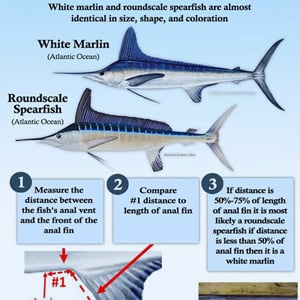
Game Fish Identification Reference Guides
Carp, grass
(Ctenopharyngodon idella)
(Ctenopharyngodon idella)

(Valenciennes, 1844); CYPRINIDAE FAMILY; also called amur, white amur, sôgyo, carpa erbivora, graskarpfen
Grass carp are native to rivers of China and Eastern Siberia (Amur River system) that flow into the Pacific Ocean between latitudes 50o to 23 o N. They have been widely introduced around the world for aquatic weed control and aquaculture purposes. Because of the potential negative impact of the fast-reproducing grass carp on sport fish, sterile (triploid) grass carp were developed. Fertilized eggs are shocked with hot or cold water or with pressure, causing them to retain an extra set of chromosomes. They are called triploid carp because they have three sets of chromosomes instead of the normal set of two. The aquatic weed control capabilities of the non-reproductive triploid grass carp appear to be essentially the same as the naturally reproducing carp. Naturally reproducing populations are reported from the Danube River in Central Europe, the Mississippi River in North America, Russia and Southern Africa.
The mullet-shaped head with a terminal mouth and no barbel, coarse dark edged scales are distinctive features of the grass carp. The dorsal fin, with 8 rays, is short and located at mid-body, above the pelvic fins. Paired anal fins are short and attached low on the body. The coloration is olivaceus to silvery white.
While the grass carp might be reluctant to bite, once hooked they are strong fish that put up a tenacious fight and are known to jump.
In some countries, grass carp are an integral part of fish culture and form an important source of fish protein for human consumption. (See also carp, common)
Grass carp are native to rivers of China and Eastern Siberia (Amur River system) that flow into the Pacific Ocean between latitudes 50o to 23 o N. They have been widely introduced around the world for aquatic weed control and aquaculture purposes. Because of the potential negative impact of the fast-reproducing grass carp on sport fish, sterile (triploid) grass carp were developed. Fertilized eggs are shocked with hot or cold water or with pressure, causing them to retain an extra set of chromosomes. They are called triploid carp because they have three sets of chromosomes instead of the normal set of two. The aquatic weed control capabilities of the non-reproductive triploid grass carp appear to be essentially the same as the naturally reproducing carp. Naturally reproducing populations are reported from the Danube River in Central Europe, the Mississippi River in North America, Russia and Southern Africa.
The mullet-shaped head with a terminal mouth and no barbel, coarse dark edged scales are distinctive features of the grass carp. The dorsal fin, with 8 rays, is short and located at mid-body, above the pelvic fins. Paired anal fins are short and attached low on the body. The coloration is olivaceus to silvery white.
While the grass carp might be reluctant to bite, once hooked they are strong fish that put up a tenacious fight and are known to jump.
In some countries, grass carp are an integral part of fish culture and form an important source of fish protein for human consumption. (See also carp, common)