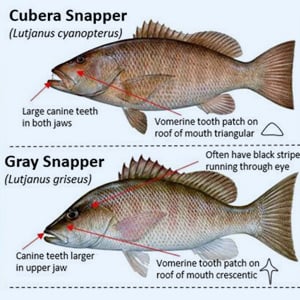
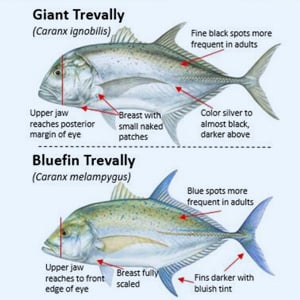
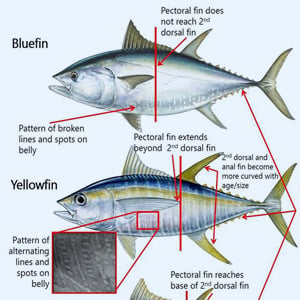
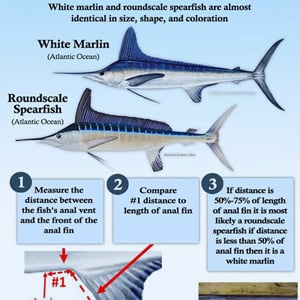
Game Fish Identification Reference Guides
Kahawai (Australian salmon)
(Arripis spp.)
(Arripis spp.)

(Forster, 1801) and / Arripis truttacea (Cuvier, 1829); ARRIPIDAE FAMILY; also called Australian salmon, black-back salmon, bay trout, sallmon trout
These species are found around New Zealand, Tasmania, and the southern portions of Australia. They inhabit continental shelf waters including estuaries, bays and inlets. They school in shallow, open coastal waters or form large surface aggregations in deeper water.
They grow to at least 3 ft (1 m) and 33 lb (15 kg), resembling a cross between a bluefish (tailor) and a southern yellowtail (called kingfish in Australia and New Zealand). The body varies from blue green or greenish to silvery with scattered dark gray, brown, or golden spots. Often mistaken for southern yellowtail, it can be quickly and easily distinguished by its lack of a yellow stripe along the body and its high first dorsal fin. The name “Australian salmon” is something of a misnomer, as it is in no way related to the true salmon or their relatives (Salmonidae).
They are highly prized by anglers and commercial fishermen. Large concentrations of feeding birds often indicate the presence of kahawai, which go into surface feeding frenzies similar to those of bluefish (tailor). They feed actively on anchovies and other small fish and can be caught on these or on fast moving lures. On light tackle, the kahawai is a very sporting catch and will leap repeatedly. It is also ideally suited to fly fishing
These species are found around New Zealand, Tasmania, and the southern portions of Australia. They inhabit continental shelf waters including estuaries, bays and inlets. They school in shallow, open coastal waters or form large surface aggregations in deeper water.
They grow to at least 3 ft (1 m) and 33 lb (15 kg), resembling a cross between a bluefish (tailor) and a southern yellowtail (called kingfish in Australia and New Zealand). The body varies from blue green or greenish to silvery with scattered dark gray, brown, or golden spots. Often mistaken for southern yellowtail, it can be quickly and easily distinguished by its lack of a yellow stripe along the body and its high first dorsal fin. The name “Australian salmon” is something of a misnomer, as it is in no way related to the true salmon or their relatives (Salmonidae).
They are highly prized by anglers and commercial fishermen. Large concentrations of feeding birds often indicate the presence of kahawai, which go into surface feeding frenzies similar to those of bluefish (tailor). They feed actively on anchovies and other small fish and can be caught on these or on fast moving lures. On light tackle, the kahawai is a very sporting catch and will leap repeatedly. It is also ideally suited to fly fishing