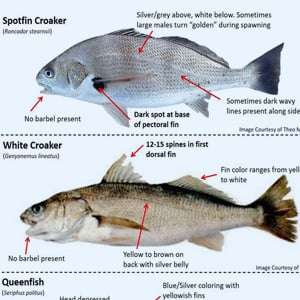
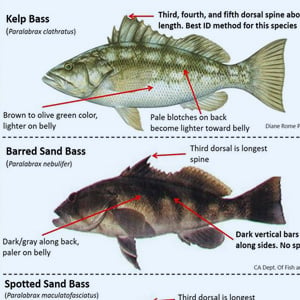
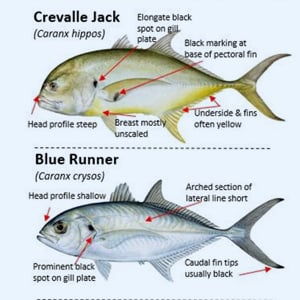
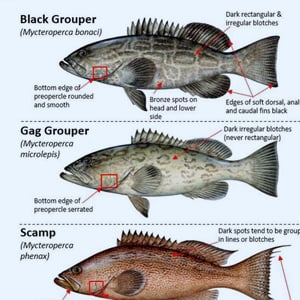
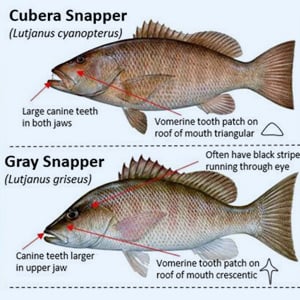
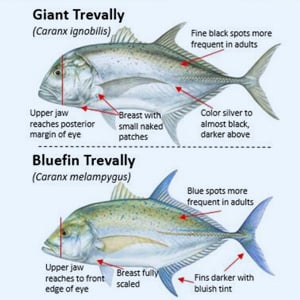
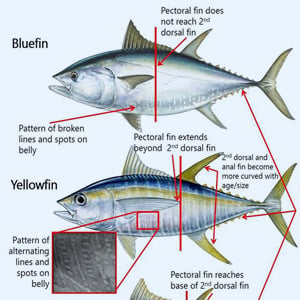
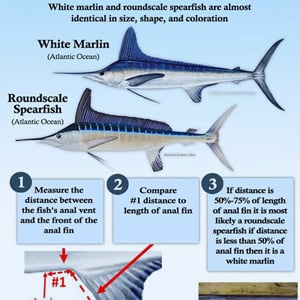
Game Fish Identification Reference Guides
Permit
(Trachinotus falcatus)
(Trachinotus falcatus)

(Linnaeus, 1758); CARANGIDAE FAMILY; also called round pompano, great pompano, Indian River permit
Occurs in the western Atlantic Ocean from Massachusetts, USA to Brazil, including the Gulf of Mexico and the West Indies. The greatest concentrations are off south Florida and it is there that the biggest specimens are taken. Permit are essentially shallow water, schooling fish occurring over sandy flats and reefs in depths of from 1 to 17 fathoms. They travel in schools of ten or more fish, though occasionally they may be seen in great numbers. They tend to become more solitary with age.
It is distinguished from the common pompano, Trachinotus carolinus, by having fewer soft rays in the dorsal and anal fins. The second dorsal fin has 1 spine and 17 21 soft rays (22 27 in the pompano). The body is laterally compressed and the second and third ribs are prominent—often as big around as one's thumb in fish weighing over 10 lb (4 5 kg). These larger ribs can be felt through the sides of the fish and help in distinguishing the permit from the pompano. In overall appearance it is a silvery fish with dusky fins, though the back is usually bluish or grayish. The ventral fins and the anterior margin of the anal fin may be orange in some specimens. Often there is a triangular yellow patch before the anal fin.
They feed in much the same way as bonefish, rooting in the sand on shallow flats. Their diet consists primarily of mollusks, crustaceans, sea urchins, and less commonly, of smaller fish.
It is a tough fighter on light tackle. When hooked it makes an initial long, fast run toward deep water, twisting and pausing to bump its head on the bottom or rub its mouth in the sand in an effort to disengage the hook. If there is coral, a sea fan, or any other obstacle on which the permit can snag the line, it will. To complicate matters, its mouth is as tough as shoe leather and it simply spits out the hook the first time there is a slack in the line.
Fishing methods include casting to fish sighted in shallow water, bottom fishing, fishing over inshore wrecks, and jigging from boats or while wading. Baits and lures include crabs, shrimp, streamer flies, bonefish jigs, weighted bucktails, and plugs. Permit up to 8 or 10 pounds are considered excellent eating
Occurs in the western Atlantic Ocean from Massachusetts, USA to Brazil, including the Gulf of Mexico and the West Indies. The greatest concentrations are off south Florida and it is there that the biggest specimens are taken. Permit are essentially shallow water, schooling fish occurring over sandy flats and reefs in depths of from 1 to 17 fathoms. They travel in schools of ten or more fish, though occasionally they may be seen in great numbers. They tend to become more solitary with age.
It is distinguished from the common pompano, Trachinotus carolinus, by having fewer soft rays in the dorsal and anal fins. The second dorsal fin has 1 spine and 17 21 soft rays (22 27 in the pompano). The body is laterally compressed and the second and third ribs are prominent—often as big around as one's thumb in fish weighing over 10 lb (4 5 kg). These larger ribs can be felt through the sides of the fish and help in distinguishing the permit from the pompano. In overall appearance it is a silvery fish with dusky fins, though the back is usually bluish or grayish. The ventral fins and the anterior margin of the anal fin may be orange in some specimens. Often there is a triangular yellow patch before the anal fin.
They feed in much the same way as bonefish, rooting in the sand on shallow flats. Their diet consists primarily of mollusks, crustaceans, sea urchins, and less commonly, of smaller fish.
It is a tough fighter on light tackle. When hooked it makes an initial long, fast run toward deep water, twisting and pausing to bump its head on the bottom or rub its mouth in the sand in an effort to disengage the hook. If there is coral, a sea fan, or any other obstacle on which the permit can snag the line, it will. To complicate matters, its mouth is as tough as shoe leather and it simply spits out the hook the first time there is a slack in the line.
Fishing methods include casting to fish sighted in shallow water, bottom fishing, fishing over inshore wrecks, and jigging from boats or while wading. Baits and lures include crabs, shrimp, streamer flies, bonefish jigs, weighted bucktails, and plugs. Permit up to 8 or 10 pounds are considered excellent eating