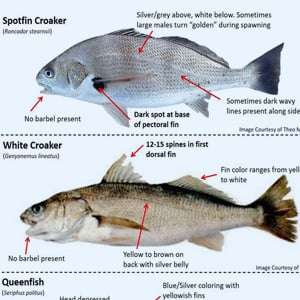
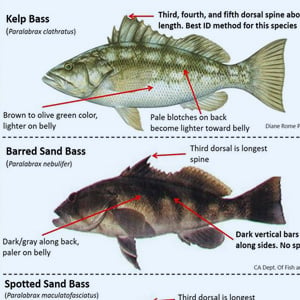
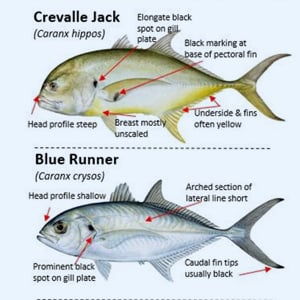
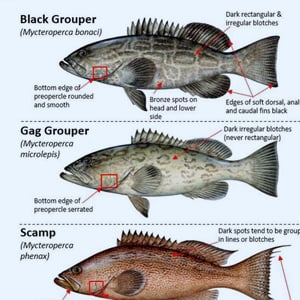
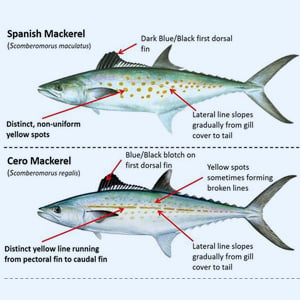
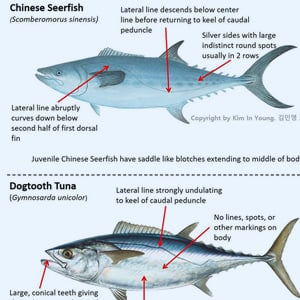
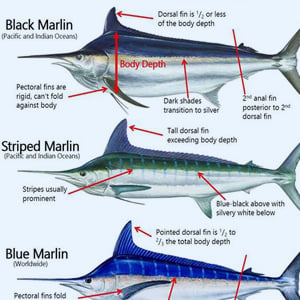
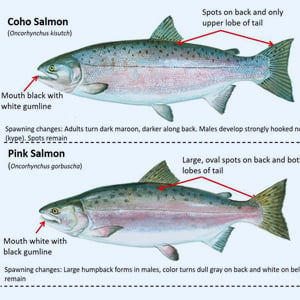
Game Fish Identification Reference Guides
Tuna, southern bluefin
(Thunnus maccoyii)
(Thunnus maccoyii)

(Castelnau, 1872); SCOMBRIDAE FAMILY; also called Japanese Central Pacific bluefin tuna
A species of the southern ocean found worldwide from 30?S to about 50?S latitude occurring in oceanic to coastal waters below thermoclines. Southern bluefin are commonly found off the southern and eastern coasts of Australia and New Zealand.
This pelagic and seasonally migratory species has been studied quite extensively in Australian waters due to its commercial importance. They spawn in the eastern Indian Ocean with one and two year old fish appearing off Western Australia in summer. Three and four year olds appear off Southern Australia in summer and New South Wales in winter. The migratory route from the Indian Ocean to the Pacific splits into two routes off southern Tasmania. Fish move either to northern New Zealand via South Island or up the Australian coast.
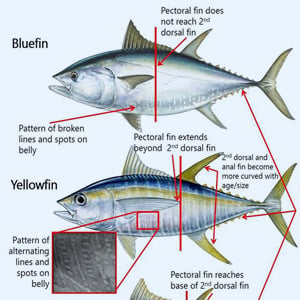
They closely resemble the Atlantic bluefin (Thunnus thynnus), and were once thought to be the same species. The difference is the number of gill rakers. The southern bluefin has a total of 31 40 on the first arch while the Atlantic bluefin has a total of 34 43. Both have in common striations on the ventral surface of the liver, short pectoral fins that do not reach to the interspace between the first and second dorsal fins, and moderate second dorsal and anal fins that are never elongated like those of the yellowfin tuna (T. albacares). The finlets are dusky yellow edged with black. It is the only species of Thunnus in which the caudal keels are bright yellow except in fish larger than 150 lb (68 kg) where the caudal keels tend to be darker.
They travel in schools of similar sized fish. Their diet consists of a variety of crustaceans, cephalopods, and fish including anchovies and pilchards.
The most popular method of catch this powerful, hard fighting fish is trolling. It can also be taken from boats or from the shore using live scombroid fishes (mackerels and little tunas) for bait. It is rarely taken on dead baits. Hooked fish are prone to fast surface runs and deep sounding.
They are excellent both as a sport fish and as table fare
A species of the southern ocean found worldwide from 30?S to about 50?S latitude occurring in oceanic to coastal waters below thermoclines. Southern bluefin are commonly found off the southern and eastern coasts of Australia and New Zealand.
This pelagic and seasonally migratory species has been studied quite extensively in Australian waters due to its commercial importance. They spawn in the eastern Indian Ocean with one and two year old fish appearing off Western Australia in summer. Three and four year olds appear off Southern Australia in summer and New South Wales in winter. The migratory route from the Indian Ocean to the Pacific splits into two routes off southern Tasmania. Fish move either to northern New Zealand via South Island or up the Australian coast.
They closely resemble the Atlantic bluefin (Thunnus thynnus), and were once thought to be the same species. The difference is the number of gill rakers. The southern bluefin has a total of 31 40 on the first arch while the Atlantic bluefin has a total of 34 43. Both have in common striations on the ventral surface of the liver, short pectoral fins that do not reach to the interspace between the first and second dorsal fins, and moderate second dorsal and anal fins that are never elongated like those of the yellowfin tuna (T. albacares). The finlets are dusky yellow edged with black. It is the only species of Thunnus in which the caudal keels are bright yellow except in fish larger than 150 lb (68 kg) where the caudal keels tend to be darker.
They travel in schools of similar sized fish. Their diet consists of a variety of crustaceans, cephalopods, and fish including anchovies and pilchards.
The most popular method of catch this powerful, hard fighting fish is trolling. It can also be taken from boats or from the shore using live scombroid fishes (mackerels and little tunas) for bait. It is rarely taken on dead baits. Hooked fish are prone to fast surface runs and deep sounding.
They are excellent both as a sport fish and as table fare