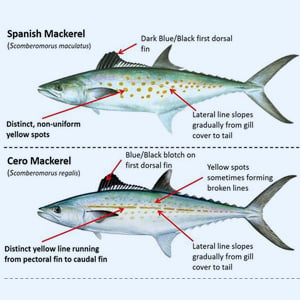
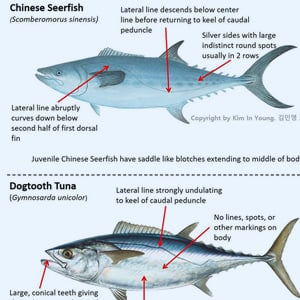
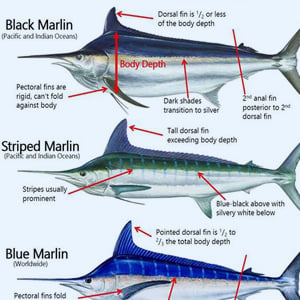
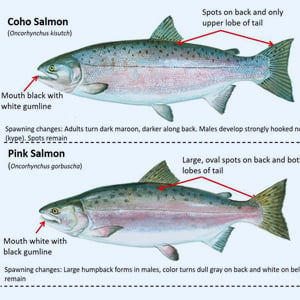
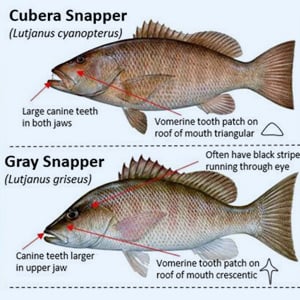
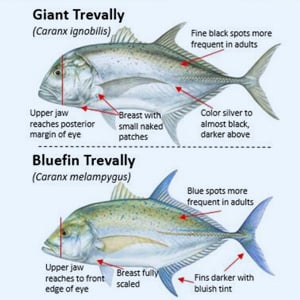
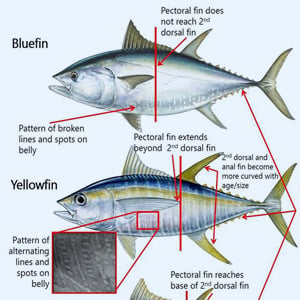
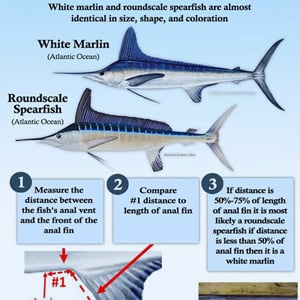
Game Fish Identification Reference Guides
Pollock
(Pollachius virens)
(Pollachius virens)

(Linnaeus, 1758): GADIDAE FAMILY; also called coalfish, Boston bluefish, green cod, blisterback, saithe, coley
Found on both sides of the Atlantic, from Greenland and Labrador to Virginia on the west side, and on the east, from Iceland to northern Spain, including the Bay of Biscay, the English Channel, and western Baltic and North Sea.
It is said to be the most active member of the cod family Gadidae. Though it occurs in shallower waters than either the cod or haddock, it is generally a deep or midwater fish occurring in depths of up to 100 fathoms. It will sometimes chase bait fish to the surface and smaller individuals are often seen milling about at the surface in large, tightly packed schools. In the western Atlantic south of Cape Cod, Massachusetts, off the U.S. east coast, pollock can be taken from depths of 25 fathoms to as little as 4 fathoms. North of Cape Cod where most of the fish are taken, they have even been caught by surf fishermen.
They can be distinguished from other members of the cod family by three features. Its lower jaw projects beyond the upper jaw, its tail is forked, and its lateral line is quite straight, not arching above the pectoral fins. Young pollock have cod like barbels on the chin, but these are small and usually disappear with age. The back varies from olive green to greenish brown. The flanks are a lighter yellowish green or gray.
Its diet consists of smaller pelagic fishes, sand eels and various crustaceans. Fishing methods include bait fishing or jigging with shrimp, herring, squid, clams, worms, or jigs, trolling or casting with spoons, tube lures, spinners, plugs, or flies. It makes strong, powerful runs and occasionally leaps and shakes. The flesh is of good quality and is commercially important.
Found on both sides of the Atlantic, from Greenland and Labrador to Virginia on the west side, and on the east, from Iceland to northern Spain, including the Bay of Biscay, the English Channel, and western Baltic and North Sea.
It is said to be the most active member of the cod family Gadidae. Though it occurs in shallower waters than either the cod or haddock, it is generally a deep or midwater fish occurring in depths of up to 100 fathoms. It will sometimes chase bait fish to the surface and smaller individuals are often seen milling about at the surface in large, tightly packed schools. In the western Atlantic south of Cape Cod, Massachusetts, off the U.S. east coast, pollock can be taken from depths of 25 fathoms to as little as 4 fathoms. North of Cape Cod where most of the fish are taken, they have even been caught by surf fishermen.
They can be distinguished from other members of the cod family by three features. Its lower jaw projects beyond the upper jaw, its tail is forked, and its lateral line is quite straight, not arching above the pectoral fins. Young pollock have cod like barbels on the chin, but these are small and usually disappear with age. The back varies from olive green to greenish brown. The flanks are a lighter yellowish green or gray.
Its diet consists of smaller pelagic fishes, sand eels and various crustaceans. Fishing methods include bait fishing or jigging with shrimp, herring, squid, clams, worms, or jigs, trolling or casting with spoons, tube lures, spinners, plugs, or flies. It makes strong, powerful runs and occasionally leaps and shakes. The flesh is of good quality and is commercially important.